Oral Surgery
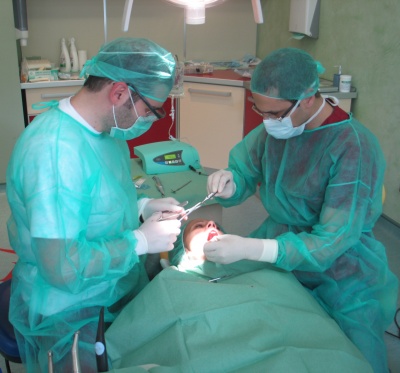 Apicoectomy
Apicoectomy
is a surgical process that removes the top of the root of the inflammatory process that is around him.
The purpose of surgery is to remove the pathological process, to prevent relapse or repetition of the process again in the same place and at the end to save the tooth, and prevent or delay its extraction.
The surgery is performed under local anesthesia or, rarely under analgosedation.
The whole process includes filling the root canal performed by a dentist, usually before surgery.
The removal of wisdom teeth
is a surgical process and is quite different from the process of the removal of erupted teeth.
There is a risk of post-operation complications, and to prevent these one should keep to and consider the following:
Wound healing is individual and variable as the occurrence of pain
The swelling is the most intense on the second or third postoperative day
Possible occurrence of pain in the neck and throat
Adjacent teeth may be temporarily sensitive
In the corner of the mouth painful cracks may develop due to the stretching of the lips during the surgery – use a lip salve
There may be a slight fever during the first 24-48 hours
Sometimes on the skin in the area of the operated tooth bruises appear
There may be a difficulty in opening the mouth and difficulty in chewing
It is advisable to avoid smoking for at least 7 days (nicotine reduces the stability of the clot and there is a real danger of its disintegration and the occurrence of extremely severe pain known as alveolitis)
24 hours after the intervention it is allowed to carefully rinse the wound after meals with warm salt water (half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water)
If there is a prolonged bleeding, inability to open the mouth, high fever, as well as an extremely large swelling, be sure to tell your doctor.
SINUS LIFT
OR ELEVATION OF THE FLOOR OF THE MAXILLARY SINUS is a surgical procedure that involves moving the bottom up of the maxillary sinus with simultaneous upgrade of the bone defect to create a sufficient height of bone necessary for implant installation.
It is used in cases of loss of teeth in the lateral regions of the upper jaw when due to the result of resorption of the alveolar ridge (premature loss of teeth and the associated reduction in the bone) or strong pneumatization of the maxillary sinus (sinus has a large volume) it is impossible to install dental implants in a way to achieve their desired stability.
This preventive technique is common in clinical practice since 1986 and is constantly modified and improved. There are several techniques of this particular surgery and the choice depends on the placement of the indications and preferences of individual operators.
The materials used for augmentation (increase in bone height) can be autologous, alloplastic, from the body (taking bone from another part of the jaw bone) or the use of artificial bone.
Of artificial materials we most commonly use products made by German manufacturer “Geistlich” which is the largest and best known global brand in this field. What is nowadays considered as a routine surgical procedure some complications are possible, though very rarely. Of these the most common is the inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus, which occurs in about 30%, others can be: hematoma, sinus membrane perforation, infection or wound dehiscence, formation of oroantral communication.
SOFT TISSUE SURGERY procedures involve operations on the mucosa, the tissue under the mucosa and the periosteum in the oral cavity. From the perspective of the proper development of tooth-muscle complex and successful prosthetic rehabilitation, the most important procedures are as follows:
FRENECTOMIA, FRENULOPLASTICA
Labial frenulum is a solid strip of fibrous tissue covered with mucous membrane that can be strongly expressed and if it is merged near the teeth the middle line, there is the possibility of a too large spacing between the first incisors (the median diastema) in the children’s ages, or in old age in case of prosthetic care the disruption of the fitting of prostheses. In these cases it is necessary to remove the frenulum, frenectomia (or at preprosthetic surgery frenuloplastica), which is a simple surgical procedure for cutting of fibrous tissue, followed by closing the wound, and the stitches are removed after a week. As for time to perform the correction of the low attachment in the upper lip frenulum with children, it is recommended to do after the emergence of the second permanent incisors.
Lingual frenulum is a strong fibrous band that connects the tongue to the floor of the oral cavity and makes it more or less immobile. In children’s age abnormal frenulum may cause slight disturbances in the function of the tongue, and if greater interference is observed, cutting the frenulum may be needed. In the case of edentulous patients expressed frenulum makes it impossible to make a stable prosthesis, because any movement of the tongue lifts the fee off. In these cases frenuloplastica is indicated, which is done in a similar way as in labial frenulum.
VESTIBULOPLASTY
The vestibule is the part between the lips and teeth and the outer reefs. The highest and deepest part is called the vestibular fornix, which is crucial in making complete dentures. In case of the loss of crestal bone or the excessive attachment of muscle fibers and the mucous membrane the fornix becomes too shallow, you cannot get proper stability and retention of the prosthesis.
The goal of vestibuloplasty is to enrich the fornix and to get the right height of the bone surface by moving the muscle attachment and tissue under the mucous membrane deeper in the fornix. As the recovery after surgery takes a long time and often leads to relapse, vestibuloplasty is done only in cases when there is no way to install the implants.